OSSE’s strategic plan is clear: foster student and staff well being. We are building OSSE’s social and emotional learning standards as the underpinning to their future implementation plan. This is largely premised on EduSolve’s SCAN Analysis Report, commissioned by OSSE to organize community assets and honor the needs of youth across the City. Through this process, various collaborative efforts were conducted; including writing groups, focus groups, in-person and virtual feedback engagements, and a survey.
Boosting Social and Emotional Learning Impact in Hopkinton Public Schools Hopkinton, Massachusetts
Hopkinton Public Schools, with a diverse student population, recognized the need to enhance their Social Emotional Learning (SEL) initiatives to better meet students’ holistic developmental needs. The primary challenge was to integrate SEL more deeply into the academic framework to promote both emotional well-being and academic success. The district faced issues with inconsistent SEL practices across schools, insufficient training for staff, and a lack of alignment with the academic goals.
EduSolve conducted a comprehensive review of existing SEL programs, gathering data through assessments, surveys, and direct observations. Working with the district team, we identified gaps in SEL curriculum alignment and inconsistencies in program delivery which were impacting student engagement and wellness.
Our team of national SEL experts conducted walkthroughs in schools, engaging with teachers and administrators to understand on-ground realities and challenges. The team evaluated the current training programs for staff, identifying areas for enhancement to support effective SEL implementation.
The project team created a phased implementation plan, ensuring that recommendations align with the district’s strategic goals and are feasible within the operational constraints. Following the implementation of the recommended strategies, Hopkinton Public Schools observed significant improvements:
- Enhanced Student Engagement: A marked increase in student participation in both academic and extracurricular activities was noted.
- Improved Emotional Well-being: Students reported higher levels of emotional satisfaction and lower stress levels, as reflected in follow-up surveys.
- Staff Empowerment: Teachers and administrators felt more confident in their abilities to integrate SEL into their teaching practices effectively.
- Academic Performance: Preliminary data indicated a positive trend in academic outcomes, correlating with improved emotional and social skills.
The partnership between Hopkinton Public Schools and EduSolve, LLC successfully enhanced the SEL framework, demonstrating the profound impact of strategic planning and targeted interventions on student development. This case study underscores the importance of a holistic approach to education, where academic success is intertwined with social and emotional well-being.
‘Tis the season to reflect on better budgeting
We are getting ready for two seasons: holiday season and budget season. In both instances, superintendents, cabinet members and board members can take time to reflect on what has worked in the immediate past and what needs to be adjusted.
The final fiscal year of ESSER invites us to do this by crafting a compelling vision for well-resourced schools with improved efficiencies. There are some predictable trends in this invitation to adjust, based on our results and the system’s response to the influx of these resources.
More often than not when the K12 system receives additional funding, it responds by spending that money on labor: new positions, new support roles, and increased compensation (including, as we saw, retention bonuses). We see this investment show up across school district strategic plans.
In 2023, we conducted a national scan of large urban school districts and found labor initiatives as second only to instructional interventions in over 80% of these plans. As pressure increases, districts also put funds into “promising practices” or innovative approaches intended to make things easier or improve performance.
During the pandemic, these practices included facility upgrades, new technologies, social and emotional learning activities, and high-quality instructional materials. Each of these expenditures needs to be tested using the Learning on Investment (LOI) measure.
Budget season to-do list

We offer these suggestions, based on our work with dozens of states and school systems:
- Map wins. Rigorously assess the LOI of each ESSER expenditure. In most districts, these include new interventionist positions, enhanced after-school and summer school offerings, increased student support, and the scaling of instructional technology. Find sustainable funds for those with a high LOI and “strategically abandon” those with low LOI. As strong innovative practices get institutionalized (e.g., the science of reading; instructional technology), intentionally reduce the high initial costs of innovation and launch such as training and equipment purchases.
- Go lean. Step back and take a hard look at ongoing – and often redundant – costs you’ve built into your budget as various assessment and information systems have been adopted. Just as cable and cellphone plans take up an increasing percentage of our household budgets, these annual costs often receive too little scrutiny in district budgeting. (Note: These redundancies create other ‘costs.’ For example, duplicative assessment and reporting practices take time away from student learning and burden staff.) These cost savings can fund some of the high-LOI activities originally funded through ESSER.
- Rethink walls. No doubt the hardest and longest conversations will be about the size of your educator workforce. Nearly every district and school has unfilled teacher and paraprofessional positions. Even with grow-your-own approaches and increased state flexibility, it is unlikely that our current educator workforce is sustainable at the national, state, local and school levels. Right-sizing the workforce is likely to consume the remainder of most superintendents’ careers and the loss of ESSER is an important trigger. Solutions will likely include adopting innovative instructional and staffing models that ensure that all students are taught by expert teachers, reducing course/program offerings in secondary grades, increasing class sizes and closing schools.
- Listen. Design and routinely use stakeholder engagement activities—not just at the governance level conducting parent engagement, community and business partner meetings, and at the school level—that encourage family engagement to understand the LOI and the trade-offs of budget choices. Routinely report on these activities and how they are informing your strategy.
- Landscape. Move beyond annual budgeting by using scenario planning to take a “what if” approach. Scenario planning smooths out short-term decision-making and helps stakeholders better understand the trade-offs. The capacity to project student enrollment by subgroup, teacher retention and recruitment by certification, capital needs and fiscal resources by source will be needed, but these will build a system-wide culture of data-driven decision-making.
In the wake of ESSER closeout, the need to improve efficiency will certainly be painful. This is a normal cycle of rebalancing similar to the one many of us experienced when the 2009 American Recovery and Reinvestment Act expired. Resilient school systems are those that adapt, innovate and become agile enough to overcome challenges. We think though that this cycle is exacerbated by the acuteness of student learning loss and the growing threat of the teacher shortage. The latter is an opportunity to prepare for another season: hiring. In the coming months, we will spotlight how states and districts are thinking about recruitment and retention in compelling ways and getting results.
Remember the adage, “Never let a good crisis go to waste.” If you oversee resource allocation, now is the time to admire the view from the cliff and find a safe path down to the valley, not step off.
Dr. Dana Godek is a seasoned expert in educational policy, social wellness, and community engagement. Her extensive career encompasses roles as a teacher, public school administrator, national researcher, and leader in federal and state policy. In her current role as the CEO of EduSolve, she applies her wealth of experience tackling intricate educational challenges in collaboration with local communities. Dana is a dedicated policy advisor to the Collaborative for Social and Emotional Learning and serves as a Data Currency Advisor to Credential Engine. She has contributed her expertise as a board member of the National Association for Federal and State Program Administrators and is a sought-after keynote speaker on matters related to federal investment in public education. Dana holds a doctorate in organizational leadership with a specialization in public policy and is a certified fundraising executive.
Michael Moore has been a national leadership and organizational development consultant and executive coach for 20 years, following a successful career as a high school principal and Superintendent of Schools. He works in school districts with ‘Directors and above’ to prioritize strategy, manage change, and build organizational capacity. As an expert in principal supervision and development, Michael co-designs culturally responsive, job-embedded leadership pathways and support models. As an expert in talent strategy and team building, he coaches executives and their teams across a wide range of organizations. Michael is a partner at the Urban Schools Human Capital Academy and works frequently with the Partnership for Leaders in Education at the UVA Darden School of Business.
End of ESSER: Why short-term fixes could create long-term crises
Americans gain an average of eight pounds over the holidays each year. Before you switch over to a fad diet, consider a bigger weight loss goal: $122 billion. Since the beginning of Elementary and Secondary School Emergency Relief (ESSER) we have been warning that when FY24 arrived, executive leadership teams would need to be ready to shed initiatives they can’t sustain and report on their Return on Investment (ROI). Teams also need to maintain those initiatives that produce Learning on Investment (LOI).
As we travel the country, we’ve been increasingly worried that superintendents and boards are waiting too long to confront the upcoming fiscal cliff. The reporting season is here, as the U.S. Department of Education just released financial reporting dates as early as March 2024 for all states.
Chief financial officers and Grants Administration leaders have been patching budgets with one-time fixes as schools returned from pandemic disruptions. Year-to-year, short-term solutions are not only causing the avoidance of hard decisions about the loss of ESSER funds but, we’d argue, they are also masking deeper, longer-term crises such as declining student enrollment, an educator workforce that is too large to sustain, and instructional offerings that are too diffuse to close learning gaps. It’s like going on a fad diet rather than making the necessary lifestyle changes.
Like getting to a healthy and sustainable weight, you’ll need to adjust both your intake and your level of activity. Communicating a compelling vision of success shared with a wide range of stakeholders will ensure better results, more satisfied families and educators, and predictable fiscal planning.
Measuring investment
ROI is a financial metric used to evaluate the profitability or efficiency of an investment relative to its cost. ROI is measured by dividing a company’s net profit by its initial investment and then multiplying the result by 100 to express the ratio as a percentage. But how to measure learning on investment (LOI)?

An LOI measure divides net student learning gains by the investment needed to generate that gain. This is a versatile process that can be applied to various scenarios, such as evaluating the performance of academic interventions, assessing the effectiveness of training programs, or comparing curricula. It guides decision-makers as they allocate resources effectively and informs choices about where to invest time, money and effort. It also identifies initiatives that need to be strategically shed to make room for fresh approaches based on the current needs of students, families and our workforce.
The fundamental challenge of public services
“Public services”— road maintenance, public safety and K12 education, for example—don’t have a “profit motive.” That absence makes it challenging but not impossible to measure the effectiveness of a public service. Historically, a particular public service will expand in scale or scope in response to political pressure and will be reduced or constrained when resources (usually tax dollars) are limited.

This push-pull dynamic can be seen as a back-and-forth between resiliency and efficiency. Resiliency in this context is the ability to respond quickly to things that aren’t predictable, such as post-pandemic student learning loss. Efficiency is simply getting the “most bang for the buck” in the most expedient ways.
There’s a negative correlation between resiliency and efficiency: when one goes up, the other goes down. Think of restaurants: they plan for efficiency, but customer volume is unpredictable and some diners want changes to what’s on the menu. School systems are facing similar changes with volume (enrollments) and modifications (requests for new services such as intervention and student well-being). That’s the challenge presented by the fiscal cliff.
ESSER was intended to improve the resiliency of K12 operations, providing for 1:1 technology, increased staffing, facility upgrades, and innovative methods and materials. The narrative of ESSER’s expiration is: “We gave you additional resources to help you through the pandemic and return to school. These resources improved your resiliency but reduced your efficiency. That’s not sustainable. Now we need you to continue moving toward a ‘new normal’ by improving your efficiency and to do that, we need to reduce your resilience.”
This superintendent’s challenge
While CFOs and federal programs directors have done a good job guiding districts through the last three years of budget tailoring, now it’s time for superintendents, cabinet members and board members to take a longer-term, strategic approach to ensure that only the most effective strategies—those with the strongest LOI—are retained as resiliency is drained from the system.
Researchers of corporate governance refer to this as “repositioning the core” of the business. LOI is not as clear-cut as ROI. Superintendents are subjected to more public scrutiny and political pressure than corporate CEOs. As such, it’s important to design a comprehensive decision-making model, maximize appropriate stakeholder engagement, push for data-driven decisions, prioritize equity, and communicate a clear and compelling vision of the future emphasizing the investment, not the reductions.
This will test even the most experienced superintendents. In our next article, we will offer practical, actionable ideas on how to get this done. But, before you stop eating all carbs, push your team to show the data wins for each initiative. It will become very clear quickly: If you can’t put it on a scale, it’s going to derail the weight loss.
Dr. Dana Godek is a seasoned expert in educational policy, social wellness, and community engagement. Her extensive career encompasses roles as a teacher, public school administrator, national researcher, and leader in federal and state policy. In her current role as the CEO of EduSolve, she applies her wealth of experience tackling intricate educational challenges in collaboration with local communities. Dana is a dedicated policy advisor to the Collaborative for Social and Emotional Learning and serves as a Data Currency Advisor to Credential Engine. She has contributed her expertise as a board member of the National Association for Federal and State Program Administrators and is a sought-after keynote speaker on matters related to federal investment in public education. Dana holds a doctorate in organizational leadership with a specialization in public policy and is a certified fundraising executive.
Michael Moore has been a national leadership and organizational development consultant and executive coach for 20 years, following a successful career as a high school principal and Superintendent of Schools. He works in school districts with ‘Directors and above’ to prioritize strategy, manage change, and build organizational capacity. As an expert in principal supervision and development, Michael co-designs culturally responsive, job-embedded leadership pathways and support models. As an expert in talent strategy and team building, he coaches executives and their teams across a wide range of organizations. Michael is a partner at the Urban Schools Human Capital Academy and works frequently with the Partnership for Leaders in Education at the UVA Darden School of Business.
Welcome to district leadership: 7 things you need to know
July is an exciting time in school districts. The students are out of school. The budget is adopted. And there are people in new leadership roles. Are you newly promoted? Are you moving from school leadership to district leadership? Congratulations!
All new roles present challenges, but in our experience the transition from the principalship to a district role feels like a very big step to many people.
In this article, we’ll look at why that’s the case. First, we’ll define district leader success criteria. Then we’ll discuss why, as the cliche says, ‘What got you here, won’t get you there.” Finally, we’ll look at the leadership shifts—in perspective, behavior and priorities—that provide a path into effective district leadership.
6 keys to district leadership
The core challenge for new district leaders is about identity. You got promoted because of your success leading adults who reported to you. While you certainly had a boss or two, you spent nearly all your time as The Boss (apologies Bruce!) at your school.
As a district leader, you’ll spend most of your time surrounded by colleagues and by more senior leaders. One newly promoted leader told us, “I used to make 30 quick decisions in a day as a principal and now every decision I need to make requires a meeting or a committee.”
As you build a new identity as a district leader, consider how will you be judged given the daily attention you’ll be getting from everyone around you. We believe these six success criteria can serve as a scorecard:
- Achievement of district goals. All district leaders are expected to understand, promote and execute the district’s goals.
- Improved student outcomes. As a school principal you had a direct impact on student outcomes. Now your impact will be less direct, but unless you’re in a purely operational role you’re still expected to improve student performance.
- Effective team functioning. Because of the transparency and cross-functional nature of district work, you’ll be judged by your ability to keep your team on-time and on-task.
- Successful cross functional work. While it’s important to know your “lane,” it’s also important to be seen as a team player by colleagues and be seen by senior leaders as someone who can manage projects.
- Sustainable initiatives. You’ll likely be expected to design and implement new projects, anticipate trends in your area of responsibility and determine what’s worth spending time and energy on. If you are implementing larger district initiatives, you will want to use strong change management practices to ensure both fidelity and sustainability.
- Stakeholder satisfaction. Getting to know your end-users and customers quickly will be critical, even if it’s your hometown (sorry again Bruce). You need to understand who they are and what they need and confirm those findings with the senior team in relation to the broader district goals.
Why is district leadership different?
Earlier, we used the cliché: “what got you here, won’t get you there.” The reason that the move from school to district leadership feels like such a big step to many leaders is because the skills that made you a successful— and promotable—principal are in some way counterproductive for district leaders.
:Superintendent turnover : Frenzy of moves as school year ends
As a principal you were able to build strong relationships with staff and students because you saw them everyday and got to know them. As a district leader, you’ll spend less time with more people making it hard to use relationships as your ‘go to’ appeal.
As a principal you could make dozens of quick decisions in a day and delegate tasks to direct reports. As a district leader, many decisions require discussion across teams or departments, stretching out the decision-making process.
As a principal you focused on things that were happening that day or as far out as the next break. You were excellent at “firefighting.” As a district leader, you are asked to think about next year and the next several years, reducing the level of urgency.
As a principal you were a generalist. You could build a master schedule, deal with an angry parent and give effective feedback to a new teacher. Except for the superintendent, district leaders are functional leaders, experts in important but narrow roles. You might be tempted to debate things that you experienced as a principal that didn’t seem quite right coming from a central office. Use these perspectives and trust your intuition with your team, but resist ‘fixing’ other departments until you know the lay of the land.
As a principal you established the political context. Others knew what was important to you, how you would react to different situations and how you managed others. As a district leader, you have been dropped into a complex political context where you don’t set the tone.
Making the shift
There is a path to becoming a successful district leader that will take at least a year to master but can be accelerated through intentional shifts in perspective and behavior. Those shifts are:
- Observe and learn the political context. You have leadership skills and capabilities but not all the context to use them effectively. Ty Wiggins, author of The New CEO offers this advice: “If it’s on fire, fix it. If it’s smoldering leave it alone until you have more context.”
- Be strategic. Lengthen your time horizon to focus on the district’s goals. Trust the managers on your team to develop the tactics for getting work done.
- Build your team. Distribute leadership across the team and make sure they can articulate and measure their goals. Provide training and coaching. Interact intentionally with them individually and collectively.
- Support your colleagues. Be curious about how they work and make decisions. Have their back in meetings. Offer opportunities to work together on small wins.
- Focus on your function but don’t become an island. We agree with Patrick Lencioni’s focus on “Team #1”—your boss and their team—but it’s also important to master your team’s specific workflow and production.
- Don’t talk about the work, do the work. Let a good ol’ dry erase board in your office talk about the work for you. Your meeting calendar will prioritize your work quickly. Don’t let it. Prioritize the work and then your calendar. The number of meetings can quickly overwhelm you. When invited, ask why your attendance is needed and how you can best prepare and participate.
- Communicate and advocate. Celebrate success. Be humble about challenges. Make it easy for others across the organization to see what you are working on and how they’re connected to it. Be sure to state your team brand and department mission in most conversations so people get to know what you’re about and where you’re taking your team.
Congratulations on moving into a bigger role. You are likely on the way to even bigger and better things!
Your results ‘hinge’ on your senior leadership team
The meeting was already 30 minutes over time. People were looking at their phones. An assistant knocked on the door and asked someone to step out. “Are we done?” the superintendent asked as he stood up. Cabinet members gathered their things and walked out, talking quietly in small groups.
The frustrated superintendent looked at us: “I don’t need any more bright ideas from people who just want to show everyone how smart they are. The board wants to know why we’re not meeting our goals. I need people who can work together to get things done. Where are the people who will execute?”
There are few things directly under a superintendent’s control, but the senior leadership team is certainly one of them. Becoming more intentional about the team’s purpose, membership and meetings will make your life easier, bring energy to the work of your leaders and improve your results.
Purpose
By design, the superintendent serves as the hinge between the board and the district’s leadership. The board oversees the process through governance and monitoring. The senior leadership team oversees performance by managing people and resources. The superintendent is the only role holding and connecting both of those functions.
Senior leadership team performance is a concern in most organizations. More than half of senior executives report underperformance by their top team. McKinsey describes the challenge as “individual and institutional biases and clunky group dynamics.” By focusing on “dynamics, not mechanics”—that is process, not just content —senior leaders can work as a team, take advantage of different skills and perspectives and bring coherence to their work.
Patrick Lencioni calls this “Team #1.” Even if you’re familiar with the concept, we encourage you to take a moment to watch this linked video and reflect on the degree to which each of your senior leaders truly behave like your team is their Team #1.
In defining the purpose or mission of your senior leadership team, span of control is often a concern. Traditionally, an ideal span of control has been seen as six or seven direct reports, but recent research has made a case for a broader scope.
This increased span has been attributed to the need for the CEO to have easier access to more information, speed up decision-making, improve operational efficiency and foster better coordination. Paradoxically, a broader span of control improves accountability because no one sits between the CEO/superintendent and the senior leader who is responsible for results.
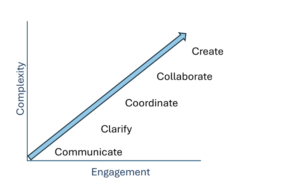 We’ve created a graphic to describe how any team should make the most of its time. The most senior teams in an organization should focus on the top-right functions – collaboration and creativity – with teams lower on the hierarchy addressing the less complex functions.
We’ve created a graphic to describe how any team should make the most of its time. The most senior teams in an organization should focus on the top-right functions – collaboration and creativity – with teams lower on the hierarchy addressing the less complex functions.
So, what should your senior leadership team collaborate on and create? The concept of time horizon comes into play here. You and your senior leaders are the only roles expected to look beyond the next 60 to 90 days. You want team members, individually and collectively, to be continuously ‘forward looking’: discussing the forces and resources in play, considering a wide range of scenarios and, pushing for rigor and creativity, but also mitigating risk. This includes making sure the senior leadership team has the superintendent’s back. Highly successful senior leaders use the time horizon to anticipate the field around the leader, both inside and out.
Senior leaders should be expected to be ‘in the arena’ with the superintendent when it comes to board member engagement, board preparation and presentations and governance-level conflict resolution. Second, similarly, as more community and stakeholder engagement becomes the norm, senior leaders should take on significant external-facing responsibilities. Expectation-setting, training and even role-playing may be needed before all members are comfortable stepping into these roles. The superintendent cannot do all the needed external-facing and political work alone.
The bottom line: The purposes of your senior leadership teams are creating long-term strategies for the district’s success, creating and collaborating on those strategies, executing and coordinating those projects and activities that lead to results, and extending the superintendent’s communication and engagement efforts with the board and community. No other teams or roles share these purposes.
Membership
You want to coach a star team, not just star players.
Corporate poet (yes, there is such a thing! ) David Whyte notes that: “Too often, we reward people who solve problems while ignoring those who prevent them. Instead of glorifying those who run around putting out fires, we need to create an organizational culture that empowers everyone to act responsibly at the first sign of smoke.” Culture, of course, starts at the top.
A strong senior leadership team has a mix of “T” and “I” shaped leaders. “I” shaped leaders have functional expertise. The CFO you trust completely with the district’s fiduciary responsibilities, for example. “T” shaped leaders successfully lead their function, while also having an organization-wide perspective: the bar across the T. If most team members are “I,” collaboration will be a challenge because everyone will “stay in their lane.” If most team members are “T,” moving from strategy to action may be a challenge.
While the “T and I” language is well known in the private sector, we suggest including a third shape (an “I” with a bar, top and bottom): those with social capital in the community, who will add values and historical perspective into the mix.
We sometimes see two membership mistakes. One is keeping a senior leader on the team who poorly represents you or the team. If you decide to commit to a “Team #1” approach it’s essential that each member’s loyalty is to the senior leadership team, not to their own team, a peer group or naysayers. As Ty Wiggins says: “Culture is the worst behavior you’ll tolerate.” And everyone watches the behavior of senior leaders.
The other mistake is to leave a mission-critical player off the senior leadership team because their title isn’t right, such as an executive director of accountability. If they’re that important to your success you should probably elevate their title, but even if you don’t, put them on the team.
Meetings
The senior leadership team is not a regular team or meeting. It is your team and meeting, and needs to meet your needs. That starts with being clear up-front about the level of decision-making. Wiggins suggests asking each team member, “Do you agree that people can disagree and still commit?” Of course, the right answer is, “Yes!” Those are the only kind of “yes men” you want on your team.
It’s important to explicitly foster a culture of vigorous debate. Be explicit about the ground rules and protocols you will use for such debate. This releases the power of the team to get the best from one another. It’s also easier when members know that the team discusses and debates, but ultimately that it’s you who will decide.
The toughest challenge in creating that culture is all leaders’ tendency to add value reflexively. Whenever possible, make your decision in the moment and unpack your reasoning. That’s a teachable moment for members and the team.
In addition to debate and decision-making, another key function of the senior leadership team is making and keeping commitments to the team. We’re fans of The 4 Disciplines of Execution but any method that records specific commitments made by members and then monitors progress will boost productivity and members’ engagement.
As professional facilitators, we plan on about two hours of preparation for each hour of meeting time and we encourage you to use a senior (but not executive) leader to play this role, ideally facilitating the meeting itself so that you can participate fully in your CEO role without managing the process. That preparation should include information-gathering, framing action items clearly, anticipating the need to bring other people into the meeting and tracking commitments from one meeting to another.
CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT
Last month, we wrote an article about how to become successful district leaders. Our Six Success Criteria provide a scorecard for how your efforts to improve the senior leadership team are working. The stronger your team, the more satisfied (and rested) you’ll be as a superintendent.
Dont’ Drift Off the Cliff, Soar to the Sky, 90 Schools, Across 5 States
Like traditional public schools, charter public schools are facing pivotal decisions, particularly given the imminent deadline of September 30, 2024, to utilize pandemic relief funds from the ESSER (Elementary and Secondary School Emergency Relief) Fund. EduSolve is proud to work with Charter Schools USA in making informed, equitable decisions amid the challenges posed by post-pandemic learning shifts and funding drop-off. In doing so, they have optimized $24M in funding. We partnered to install tangible system solutions and sustainability measures that measure ROI to preserve LOI.
Why Every School Leader Needs Executive Leadership Coaching
In the ever-evolving landscape of education, school leaders face numerous challenges that require a unique set of skills and a deep understanding of their roles. The responsibilities of a school leader extend far beyond administrative tasks; they encompass shaping the future of students, fostering a positive learning environment, and ensuring the professional growth of teachers. This is where executive leadership coaching comes into play. In this article, we will explore why every school leader needs executive leadership coaching and how it can make a significant impact on their performance and the overall success of their schools.
Understanding Executive Leadership Coaching
Executive leadership coaching is a personalized, one-on-one developmental process designed to enhance the leadership skills and capabilities of executives. In the context of education, this coaching is tailored specifically for school leaders, including principals, vice-principals, and other administrative staff. The coaching process involves working with a professional coach who helps the school leader identify their strengths and weaknesses, set goals, and develop strategies to achieve those goals.
Also Read: Why is Executive Coaching Important for Superintendents and School District Leaders?
The Role of a School Leader
Before delving into the benefits of executive leadership coaching, it is essential to understand the multifaceted role of a school leader. School leaders are responsible for:
- Setting the Vision and Goals: They establish the vision and goals for the school, aligning them with the broader educational objectives and ensuring that they are communicated effectively to all stakeholders.
- Creating a Positive School Culture: A positive school culture is critical for student success. School leaders play a vital role in fostering an environment where students feel safe, valued, and motivated to learn.
- Managing Resources: Effective resource management, including budgeting, staffing, and facilities management, is crucial for the smooth functioning of the school.
- Supporting Teachers: School leaders are responsible for the professional development and support of teachers, ensuring that they have the necessary resources and training to deliver high-quality education.
- Engaging with the Community: Building strong relationships with parents, community members, and other stakeholders is essential for creating a supportive and collaborative educational environment.
Why Every School Leader Needs Executive Leadership Coaching
1. Enhancing Leadership Skills
One of the primary reasons why school leaders need executive leadership coaching is to enhance their leadership skills. Effective leadership is not an innate quality but a skill that can be developed and refined over time. Coaching helps school leaders identify their strengths and areas for improvement, providing them with the tools and strategies to become more effective leaders.
2. Improving Decision-Making Abilities
School leaders are required to make numerous decisions daily, many of which have a significant impact on the school community. Executive leadership coaching helps leaders develop critical thinking and decision-making skills, enabling them to make informed and strategic decisions that benefit the school and its students.
3. Promoting Personal and Professional Growth
Executive leadership coaching promotes both personal and professional growth. Through coaching, school leaders gain self-awareness and a deeper understanding of their leadership style. This self-awareness is crucial for personal growth and development, allowing leaders to build on their strengths and address their weaknesses.
4. Building Resilience
The role of a school leader can be highly demanding and stressful. Executive leadership coaching provides leaders with the support and strategies needed to build resilience and effectively manage stress. Resilient leaders are better equipped to handle challenges and setbacks, ensuring the long-term success of the school.
5. Fostering a Positive School Culture
A positive school culture is essential for student success and well-being. Executive leadership coaching helps school leaders develop the skills and strategies needed to create and maintain a positive school culture. This includes fostering open communication, promoting inclusivity, and encouraging collaboration among staff and students.
6. Enhancing Communication Skills
Effective communication is a cornerstone of successful leadership. Executive leadership coaching helps school leaders develop strong communication skills, enabling them to convey their vision and goals clearly, build strong relationships with staff and students, and engage with the broader school community.
7. Supporting Teacher Development
Teachers are at the heart of the educational process, and their professional development is critical for student success. Executive leadership coaching helps school leaders develop strategies to support and mentor teachers, providing them with the resources and training needed to excel in their roles.
8. Achieving Work-Life Balance
Balancing the demands of a leadership role with personal life can be challenging. Executive leadership coaching provides school leaders with the tools and strategies needed to achieve a healthy work-life balance, ensuring that they can perform at their best without compromising their well-being.
9. Driving School Improvement
Ultimately, the goal of executive leadership coaching is to drive school improvement. By enhancing the leadership capabilities of school leaders, coaching helps create a positive and effective learning environment that benefits students, teachers, and the broader school community.
Also Read: Empower Your Career with Executive Leadership Training at PMOC
The Process of Executive Leadership Coaching
The process of executive leadership coaching typically involves several stages:
1. Initial Assessment
The coaching process begins with an initial assessment to identify the school leader’s strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. This assessment may involve self-evaluation, feedback from colleagues and staff, and other diagnostic tools.
2. Goal Setting
Based on the initial assessment, the coach and school leader work together to set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. These goals provide a clear direction for the coaching process and serve as benchmarks for measuring progress.
3. Developing Action Plans
Once the goals are established, the coach helps the school leader develop action plans to achieve these goals. This involves identifying specific strategies, resources, and support needed to reach the desired outcomes.
4. Implementing and Monitoring
The school leader implements the action plans with ongoing support and guidance from the coach. Regular monitoring and feedback are essential to track progress and make necessary adjustments to the plans.
5. Reflecting and Evaluating
The coaching process includes regular reflection and evaluation to assess the effectiveness of the coaching and the progress made towards the goals. This helps ensure continuous improvement and development.
The Future of Executive Leadership Coaching in Education
As the educational landscape continues to evolve, the need for effective leadership becomes increasingly critical. Executive leadership coaching is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of education by empowering school leaders with the skills and strategies needed to navigate the complexities of their roles.
Embracing Technology
The future of executive leadership coaching in education will likely see an increased integration of technology. Virtual coaching sessions, online resources, and digital assessment tools can make coaching more accessible and convenient for school leaders.
Customizing Coaching Programs
Customized coaching programs tailored to the specific needs and contexts of individual school leaders will become more prevalent. This personalized approach ensures that coaching is relevant and impactful, addressing the unique challenges and goals of each leader.
Fostering Collaborative Leadership
The future of executive leadership coaching will emphasize the importance of collaborative leadership. School leaders will be encouraged to build strong teams, foster collaboration among staff, and engage with the broader school community to create a supportive and inclusive educational environment.
Promoting Continuous Learning
Executive leadership coaching will continue to promote a culture of continuous learning and development. School leaders will be encouraged to seek ongoing professional development opportunities, stay updated with the latest educational trends, and continuously refine their leadership skills.
Conclusion
In conclusion, executive leadership coaching is an invaluable resource for school leaders. It provides them with the tools, strategies, and support needed to enhance their leadership skills, improve decision-making abilities, and foster a positive school culture. By investing in executive leadership coaching, schools can ensure that their leaders are well-equipped to navigate the challenges of their roles and drive school improvement. As the educational landscape continues to evolve, the importance of effective leadership cannot be overstated. Executive leadership coaching is a powerful tool that can help school leaders achieve their goals and create a positive and effective learning environment for students, teachers, and the broader school community.
Elevate Your Leadership Potential Today
Are you ready to transform your leadership skills and drive your school towards success? Our Executive Leadership Training program is designed to empower school leaders with the tools and strategies needed to create a positive and effective educational environment.
Don’t wait—take the first step towards becoming an exceptional leader.
Enroll Now and start your journey to excellence in school leadership.
For more information or to speak with one of our expert coaches, Contact Us today. Together, we can build a brighter future for your school.
Also Read: Executive Coaching for School Leaders: Cultivating Tomorrow’s Educational Visionaries
Why is it Important to Teach Social and Emotional Skills in School?
In today’s fast-paced world, academic skills alone are not enough for children to succeed. Schools are increasingly recognizing the importance of teaching social and emotional skills alongside traditional subjects like math, science, and language arts. But why is it important to teach social and emotional skills in school? This blog will delve into the significance of these skills, the benefits they bring to students, and how they can be effectively integrated into the school curriculum.
Understanding Social and Emotional Skills
Social and emotional skills, often referred to as Social and Emotional Learning (SEL), encompass a range of abilities that help individuals manage their emotions, build healthy relationships, and make responsible decisions. Key components of SEL include:
- Self-Awareness: Recognizing one’s emotions, strengths, and limitations.
- Self-Management: Regulating emotions, setting goals, and managing stress.
- Social Awareness: Understanding and empathizing with others from diverse backgrounds.
- Relationship Skills: Building and maintaining healthy relationships.
- Responsible Decision-Making: Making ethical and constructive choices.
Also Read: Why Social and Emotional Learning Matters: A Deep Dive
The Importance of Teaching Social and Emotional Skills
Enhancing Academic Performance
Research has shown that students who develop strong social and emotional skills tend to perform better academically. When children can manage their emotions and behaviors, they are more focused and engaged in the classroom. SEL programs help reduce behavioral problems, allowing teachers to spend more time on instruction and less on discipline.
Promoting Mental Health
Mental health issues such as anxiety and depression are on the rise among young people. Teaching social and emotional skills provides students with tools to cope with stress, build resilience, and seek help when needed. This proactive approach to mental health can lead to better long-term outcomes for students.
Fostering Positive Relationships
Social and emotional skills are crucial for building and maintaining positive relationships. By learning empathy, communication, and conflict resolution, students can form healthier connections with peers, teachers, and family members. These skills help create a more inclusive and supportive school environment.
Preparing for the Future
The modern workplace requires more than technical skills; employers are looking for individuals who can collaborate, adapt, and solve problems. SEL prepares students for the future by developing these essential soft skills. Students who excel in SEL are more likely to succeed in their careers and personal lives.
Benefits of Social and Emotional Learning
Improved Academic Outcomes
Numerous studies have shown that SEL programs can lead to significant improvements in students’ academic performance. For example, a meta-analysis of 213 studies involving over 270,000 students found that those who participated in SEL programs had an 11 percentile-point gain in academic achievement compared to those who did not participate.
Reduced Behavioral Problems
SEL programs help reduce disruptive behaviors and increase positive social interactions. Schools that implement SEL report fewer instances of bullying, violence, and disciplinary actions. Students learn to manage their emotions and resolve conflicts peacefully, creating a safer and more conducive learning environment.
Enhanced Emotional Well-Being
Students who develop social and emotional skills report higher levels of emotional well-being. They experience lower levels of anxiety and depression and have a greater sense of self-worth. SEL helps students develop a positive outlook on life and build the resilience needed to overcome challenges.
Better Social Relationships
Social and emotional skills are fundamental for building strong, healthy relationships. Students who excel in SEL are better equipped to communicate effectively, empathize with others, and work collaboratively. These skills are essential for forming friendships, working in teams, and building a supportive community.
Increased Civic Engagement
SEL also fosters a sense of social responsibility and civic engagement. Students learn to understand and appreciate diverse perspectives, which can lead to greater involvement in community service and other civic activities. This prepares students to be active, responsible citizens.
Also Read: What Happens When a Child Lacks Social Emotional Development?
Integrating SEL into the School Curriculum
Creating a Supportive Environment
A supportive school environment is crucial for effective SEL implementation. This involves creating a safe, inclusive, and respectful atmosphere where students feel valued and understood. Schools can promote positive behavior and create a sense of belonging by celebrating diversity and encouraging kindness and empathy.
Professional Development for Teachers
Teachers play a key role in delivering SEL programs. Providing professional development opportunities helps teachers understand the principles of SEL and how to integrate them into their teaching practices. Training can include workshops, coaching, and collaborative learning opportunities.
Incorporating SEL into Daily Activities
SEL should be woven into the fabric of the school day rather than treated as a separate subject. This can be done by incorporating SEL principles into daily activities, such as:
- Morning Meetings: Starting the day with a morning meeting where students share their feelings and set goals.
- Classroom Discussions: Integrating SEL topics into classroom discussions and activities.
- Collaborative Projects: Encouraging teamwork and cooperation through group projects.
- Reflection Time: Providing time for students to reflect on their emotions and experiences.
Using Evidence-Based Programs
Many evidence-based SEL programs are available that have been proven to be effective. Schools can choose from programs such as Second Step, PATHS (Promoting Alternative Thinking Strategies), and CASEL (Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning). These programs provide structured lessons and activities to help students develop SEL skills.
Engaging Families and Communities
Involving families and communities in SEL initiatives can enhance their effectiveness. Schools can engage parents through workshops, newsletters, and family activities that reinforce SEL principles at home. Collaborating with community organizations can also provide additional resources and support for SEL programs.
Challenges and Considerations
Balancing Academic and SEL Priorities
One of the challenges schools face is balancing the time and resources devoted to academic instruction and SEL. However, integrating SEL into the curriculum does not have to come at the expense of academic learning. In fact, SEL can enhance academic outcomes by creating a more positive and effective learning environment.
Addressing Diverse Needs
Students come from diverse backgrounds and have varying needs. SEL programs must be flexible and culturally responsive to address the unique experiences and challenges faced by different student populations. This includes considering factors such as race, ethnicity, gender, and socioeconomic status.
Measuring SEL Outcomes
Assessing the effectiveness of SEL programs can be challenging. Unlike academic skills, social and emotional skills are not easily measured through standardized tests. Schools can use a variety of assessment tools, such as surveys, observations, and self-report measures, to evaluate the impact of SEL programs on students’ well-being and behavior.
Success Stories and Case Studies
The Impact of SEL in Elementary Schools
Several elementary schools across the United States have successfully integrated SEL into their curriculum with positive results. For example, an elementary school in Illinois implemented the Second Step program and reported a significant decrease in behavioral problems and an increase in students’ social skills and academic performance.
SEL in Middle and High Schools
Middle and high schools have also seen the benefits of SEL. A high school in California introduced the RULER program (Recognizing, Understanding, Labeling, Expressing, and Regulating emotions) and observed improvements in students’ emotional intelligence, relationships, and academic outcomes. The program helped students develop a better understanding of their emotions and how to manage them effectively.
Community-Wide SEL Initiatives
Some communities have taken a comprehensive approach to SEL by implementing it across multiple schools and community organizations. In Austin, Texas, the school district partnered with local nonprofits to provide SEL training for teachers, students, and families. This community-wide initiative led to improved student behavior, academic performance, and overall well-being.
Conclusion
Teaching social and emotional skills in school is essential for preparing students for success in both their academic and personal lives. SEL programs help enhance academic performance, promote mental health, foster positive relationships, and prepare students for the future. By creating a supportive environment, providing professional development for teachers, incorporating SEL into daily activities, using evidence-based programs, and engaging families and communities, schools can effectively integrate SEL into their curriculum. Despite challenges, the benefits of SEL are clear, and its impact on students’ lives is profound. As we continue to navigate the complexities of the modern world, equipping students with the social and emotional skills they need is more important than ever.
Certified Grants Management Specialist Training: Your Path to Expert Grant Administration
In the realm of non-profit organizations, educational institutions, and government agencies, securing and managing grants is a crucial aspect of sustaining operations and funding initiatives. Effective grant management ensures that funds are utilized efficiently and in compliance with all relevant regulations. For professionals seeking to excel in this field, obtaining certification as a Grants Management Specialist is a valuable step. This article explores the benefits, components, and career prospects of Certified Grants Management Specialist Training.
Understanding Grants Management
Grants management involves the processes of planning, securing, and overseeing grant funds awarded to organizations. This includes tasks such as writing proposals, budgeting, reporting, and ensuring compliance with grant terms and conditions. Effective grants management is vital for maximizing the impact of the awarded funds and maintaining the trust of funding bodies.
Also Read: What is MTSS for Teachers?
The Importance of Certification
Becoming a Certified Grants Management Specialist demonstrates a high level of expertise and commitment to the field. Certification offers several advantages:
- Enhanced Credibility: Certification is a testament to your knowledge and skills, enhancing your credibility with employers and funding organizations.
- Career Advancement: Certified professionals are often preferred for higher-level positions and leadership roles in grants management.
- Updated Knowledge: Certification programs ensure that you stay current with the latest regulations, best practices, and technological advancements in grants management.
- Networking Opportunities: Certification programs often include memberships in professional organizations, providing valuable networking opportunities.
Components of Certified Grants Management Specialist Training
Certified Grants Management Specialist Training programs are designed to equip professionals with the comprehensive knowledge and skills needed for effective grants administration. Key components of these programs typically include:
- Grant Proposal Writing: Training in crafting compelling grant proposals that effectively communicate the needs and goals of your organization.
- Budgeting and Financial Management: Learning to develop accurate budgets and manage grant funds in compliance with financial regulations.
- Compliance and Reporting: Ensuring adherence to grant terms, conditions, and reporting requirements to maintain funding and avoid penalties.
- Grant Monitoring and Evaluation: Techniques for monitoring grant-funded projects and evaluating their outcomes to demonstrate impact and inform future proposals.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating risks associated with grant-funded projects to ensure successful outcomes.
Also Read: What are the 6 Domains of MTSS?
Career Prospects and Opportunities
The demand for skilled grants management specialists is on the rise across various sectors. Certified professionals can pursue diverse career paths, including:
- Grants Manager: Overseeing the entire grants management process within an organization.
- Grant Writer: Specializing in writing grant proposals to secure funding for projects and initiatives.
- Compliance Officer: Ensuring that organizations adhere to all grant-related regulations and requirements.
- Program Manager: Managing specific grant-funded programs and projects from inception to completion.
- Consultant: Providing expert advice and services to organizations seeking to improve their grants management practices.
Choosing the Right Training Program
When selecting a Certified Grants Management Specialist Training program, consider the following factors:
- Accreditation: Ensure that the program is accredited by a reputable organization in the field of grants management.
- Curriculum: Review the curriculum to ensure it covers all essential aspects of grants management.
- Instructors: Look for programs taught by experienced professionals with a proven track record in grants management.
- Flexibility: Consider programs that offer flexible learning options, such as online courses, to accommodate your schedule.
- Support and Resources: Choose a program that provides ongoing support, resources, and networking opportunities for graduates.
Conclusion
Certified Grants Management Specialist Training is an invaluable investment for professionals seeking to advance their careers in grants management. By gaining certification, you demonstrate your expertise, enhance your career prospects, and contribute to the effective administration of grant funds. Whether you are a seasoned professional or new to the field, obtaining certification is a strategic step towards achieving your career goals and making a meaningful impact in your organization.
Explore the Certified Grants Management Specialist Training program at Edu-Solve to take your grants management skills to the next level and unlock new opportunities in this dynamic field.
Also read: Why Social and Emotional Learning Matters: A Deep Dive