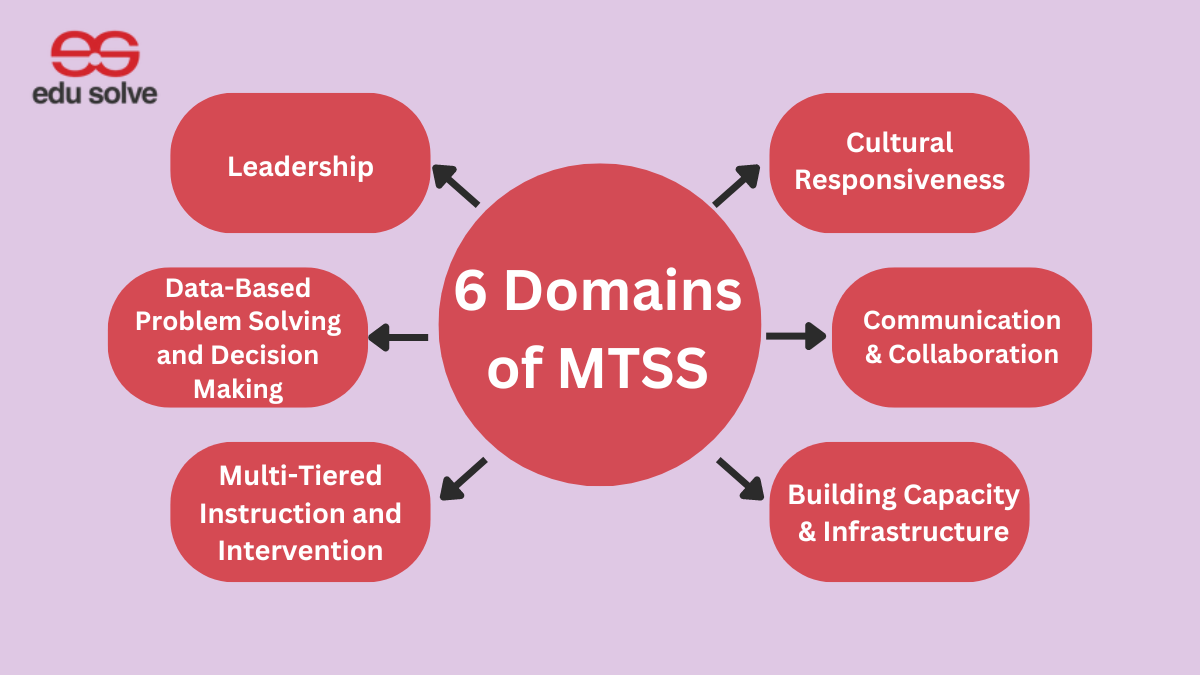
The educational landscape has changed recently to meet kids’ varied behavioral and academic requirements. Multi tiered systems of support education are one of the most effective and revolutionary strategies that have become well-known in this arena. This framework—often abbreviated as MTSS—is intended to give kids a methodical and regulated way to receive different levels of help according to their unique requirements.
The idea, elements, methods of implementation, and advantages of Multi Tiered Systems of Support schooling will all be covered in this blog. Promoting inclusive and productive learning settings requires an awareness of this concept, regardless of your role as a parent, educator, administrator, or legislator.
What is Multi Tiered Systems of Support Education?
It ensures that every kid receives the assistance they require to succeed in school by working through several “tiers” or levels of support.
To establish a unified system of support, the MTSS framework incorporates several educational programs, including Response to Intervention (RTI) and Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS). It is distinguished by evidence-based interventions, team-based problem-solving, and ongoing monitoring.
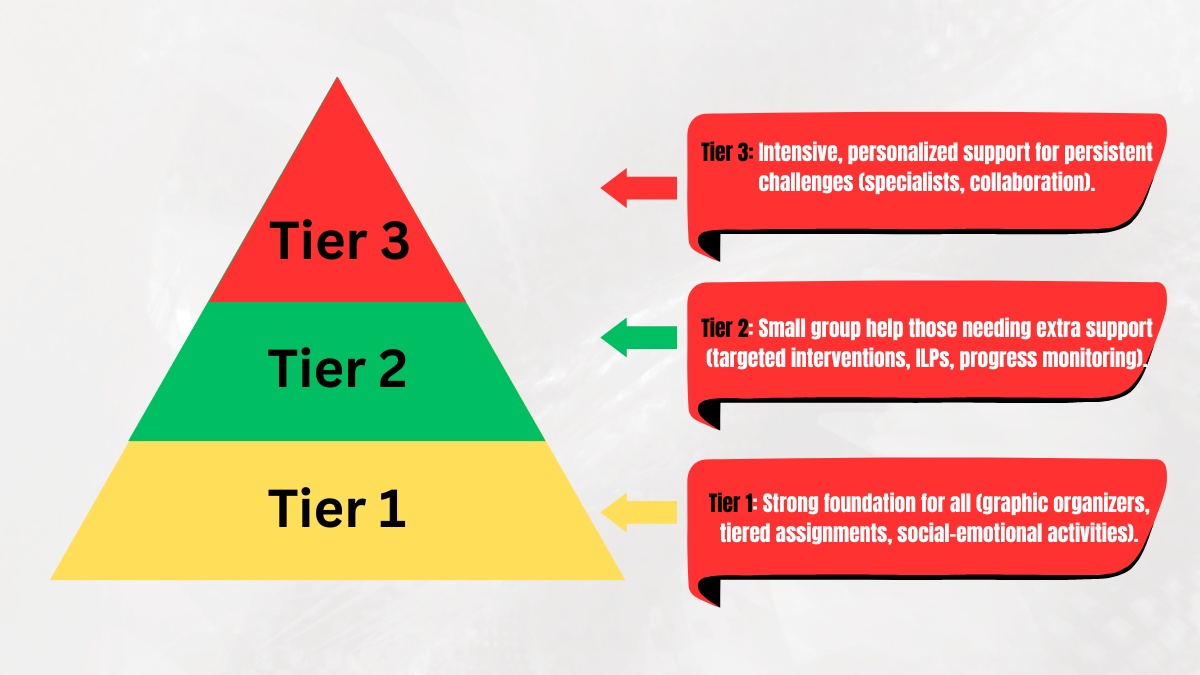
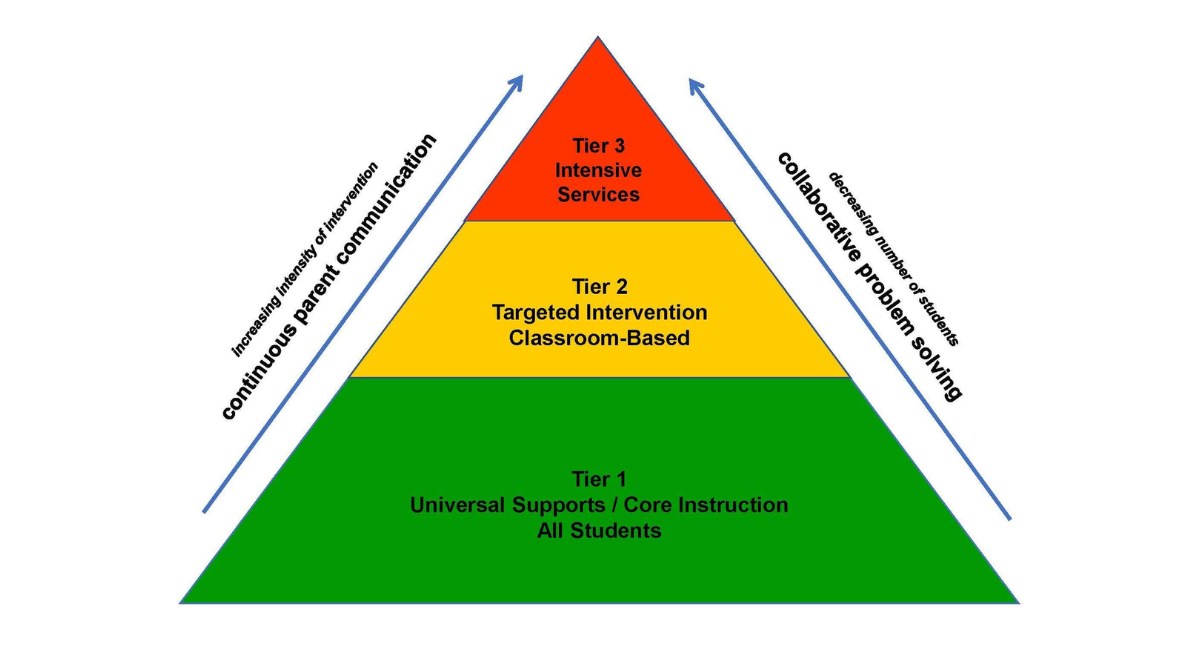
The Three Tiers of MTSS
MTSS usually functions at three levels:
Tier 1: Universal Support
All kids in a general education environment receive top-notch, research-based instruction and behavioral support as part of Tier 1. Prevention and early detection are the main goals.
Strategies for an inclusive classroom
The core curriculum
All-inclusive screenings
Tier 2: Targeted Support
Tier 1 students who don’t advance enough are transferred to Tier 2. In small groups, this level offers focused interventions.
- Temporary assistance
- Frequent tracking of progress
- Focused learning or group sessions
Tier 3: Intensive Support
Students with substantial needs who have not responded to Tier 2 therapies are placed in this tier. Individualized and comprehensive support is provided.
- Individual interventions
- Plans for Individualized Education (IEPs)
- specialized training from qualified personnel
Multi Tiered Systems of Support education guarantees that interventions are given early, before issues worsen, by organizing support in this way.
Key Components of Multi Tiered Systems of Support Education
- Screening and Assessment
Tools for universal screening assist in identifying pupils who might require more assistance.
- Evidence-Based Practices
Research must provide a strong foundation for interventions and instructional practices.
- Collaboration and Teaming
To satisfy the needs of students, administrators, parents, teachers, and experts must collaborate.
- Fidelity of Implementation
Interventions must be implemented as planned, consistently, and honorably.
- Family Engagement
Student success is more likely when families are included in the support process.
The Role of Educators in MTSS
The front-line employees in multi-tiered support education systems are teachers. Among their duties are:
- Effectively delivering core instruction
- Tracking the development of students
- Speaking with families
- Working together with intervention teams
- Putting specific strategies into practice
Professional development and continual training are crucial for ensuring that educators are equipped to fulfill their duties in the MTSS framework.
Benefits of Multi Tiered Systems of Support Education
The entire school ecosystem benefits from the use of Multi Tiered Systems of Support education.
- Improved Student Outcomes: MTSS serves all students and helps close achievement gaps.
- Data-Driven Practices: Based on actual data, schools make well-informed judgments.
- Equity and Inclusion: Every student gets the amount of assistance they require.
- Professional Collaboration: Promotes a collaborative approach to teaching.
Common Challenges in MTSS Implementation
Despite its advantages, MTSS implementation may present several difficulties for schools:
- Insufficient training for employees
- Not enough resources
- Intervention time limits
- Unreliable data monitoring
- Low levels of familial involvement
Community involvement, appropriate financial allocation, and dedication from school leadership are necessary to overcome these obstacles.
Integrating Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) with MTSS
Academic, behavioral, and social-emotional components are all included in a thorough Multi Tiered Systems of Support educational paradigm. By incorporating SEL with MTSS, one can develop:
- The capacity for emotional intelligence
- Good connections
- Adaptability
- Making responsible decisions
A more comprehensive approach to student development can be achieved by including SEL interventions into each of the three support tiers.
How Schools Can Implement MTSS Successfully
Step 1: Build Leadership Support
Start by having school administrators comprehend and support the MTSS approach.
Step 2: Create a Vision
Establish precise objectives and success standards for the execution.
Step 3: Train Staff
Give staff members and teachers professional development opportunities.
Step 4: Use Data Systems
Put in place mechanisms for gathering, analyzing, and reporting data.
Putting Multi Tiered Systems of Support education into practice is a process rather than a one-time thing.
Real-World Example: MTSS in Action
To address declining reading scores, educators at an Illinois elementary school used Multi Tiered Systems of Support instruction. Within a single academic year, reading proficiency rose by 20% thanks to targeted Tier 2 interventions, small group instruction, and universal screening. Consistent observation and cooperation between parents, teachers, and administrators were essential to the outcome.
The Future of MTSS in Education
Multi Tiered Systems of Support education will continue to be a crucial foundation in upcoming educational reforms due to the rising demand for inclusive learning environments and individualized instruction. Since technology has been incorporated, schools can now:
- Automate the process of gathering data.
- Customize your lesson plans.
- Real-time communication with families
- Offer virtual interventions.
To better serve each learner, MTSS will adjust as educational needs change.
Final Thoughts
Multiple Support Tiers Education is a dedication to educational excellence and equity, not merely a tactic. Multi tiered systems of support education change the way schools serve their children by offering the appropriate amount of support at the appropriate moment. The model incorporates families, empowers teachers, and—above all—creates a learning environment where each student may succeed.