The value of social and emotional growth has become more recognized in the field of education in recent years. Schools and educators today understand that kids’ emotional intelligence, self-awareness, and interpersonal abilities are closely linked to their academic achievement. Components of social emotional learning, a framework that fosters critical life skills outside of the classroom, were born out of this idea.
The components of social emotional learning, which serve as the foundation for students’ academic success, resilience, and general well-being, are at the center of this framework. Understanding these elements is essential for developing emotionally knowledgeable, sympathetic, and socially conscious people, regardless of your role as a parent, educator, counselor, or legislator.
What is Social Emotional Learning (SEL)?
It’s critical to comprehend the true meaning of social emotional learning (SEL) before delving into its components. The Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL) defines SEL as the process by which people gain and use the abilities, attitudes, and information required to:
- Recognize and control your feelings
- Establish and accomplish constructive goals.
- Empathize with and feel for other people.
- Create and preserve wholesome connections
- Make wise choices.
This all-encompassing method guarantees that students are prepared for life as well as for school. SEL includes social responsibility, ethical decision-making, and emotional intelligence in addition to academics.
Why Are Components of Social Emotional Learning Important?
Extensive research supports the substantial benefits of SEL. Students who participate in successful SEL programs exhibit enhanced classroom behavior, better academic achievement, more capacity to cope with stress and sadness, and more positive attitudes about both others and themselves.
But how are these advantages achieved? The key is to successfully include the components of social emotional learning into regular teaching and learning activities.
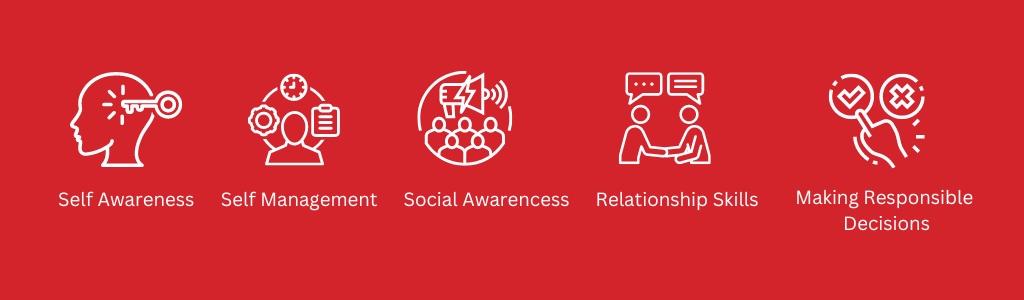
The Five Core Components of Social Emotional Learning
The five fundamental elements listed by CASEL serve as the cornerstone of successful SEL practices. Every element stands for an essential set of abilities for social and emotional growth.
1. Self-Awareness
Accurate evaluation of one’s advantages and disadvantages is also part of this.
Key elements of self-awareness include:
- Recognizing feelings
- Understanding one’s values and beliefs
- Perception of oneself accurately
- Increasing self-assurance
Strong self-awareness enables a pupil to examine their actions, identify emotional triggers, and overcome obstacles more skillfully.
2. Self-Management
Edusolve is here to help you achieve goals and dreams.
Important components of self-management consist of:
- Control of emotions
- Establishing and achieving goals
- Control of impulses
- Motivation and self-control
This element supports students in managing their frustration, maintaining focus in class, and persevering through social and academic obstacles.
3. Social Awareness
The capacity to sympathize with people from different backgrounds and cultures is known as social awareness. It also entails identifying resources and supports in one’s surroundings as well as comprehending social norms.
Important components of social awareness include:
- Compassion and empathy
- Observance of diversity
- Recognizing moral and societal standards
- Understanding the viewpoints of others
Pupils with high social awareness are more likely to participate in constructive communal behavior, are more inclusive, and perform better on group tasks.
4. Relationship Skills
Effective communication, teamwork, resolving conflicts, and asking for assistance when necessary are all part of this.
- Significant elements of relational skills consist of:
- Speaking and hearing
- Cooperation and teamwork
- Resolving conflicts
- Creating and preserving friendships
Students who possess strong interpersonal skills are able to encourage their peers, collaborate in groups, and resolve conflicts in educational settings.
5. Responsible Decision-Making
Making morally sound decisions regarding one’s own and other people’s conduct is a key component of responsible decision-making. It involves the capacity to assess the effects of decisions, think about other people’s welfare, and analyze situations.
- Among the essential components of making responsible decisions are:
- Identification of the problem
- Critical analysis and assessment
- Thinking introspectively
- Responsibility for ethics
Pupils who are proficient in this area are more likely to make decisions that are consistent with their values and objectives and are less likely to act in ways that are dangerous.
Integrating Components of Social Emotional Learning in the Classroom
It’s just half the battle to understand the elements of social emotional learning. Careful incorporation into the curriculum, school culture, and classroom activities yields the greatest benefit.
Teachers can include SEL components in the following ways:
1. Morning Meetings or Check-ins
By giving kids a secure place to express their feelings and listen to others, they foster self-awareness and interpersonal skills.
2. Project-Based Learning
Through practical problem-solving, collaborative tasks foster the development of social awareness, interpersonal skills, and responsible decision-making.
3. Mindfulness and Reflection Activities
Journaling and breathing techniques are examples of activities that foster self-awareness and self-management.
4. Conflict Resolution Workshops
Empathy and relationship-building are taught through role-playing and facilitated conversations about settling disputes.
Benefits of Teaching the Components of Social Emotional Learning
There are several long-term advantages to integrating social-emotional learning components into educational systems:
Academic Gains: Test scores and grades are higher for students who receive SEL help.
Reduced Behavioral Problems: Reduced instances of disruptive behavior, absenteeism, and bullying.
Stronger Communities: Encourages civic engagement, empathy, and inclusivity.
Social Emotional Learning at Home and in the Community
Classrooms are not the only setting for SEL.
- Parents Can:
Set an example of appropriate behavior and emotional control.
Encourage candid discussions about emotions.
Give helpful criticism.
Encourage and commend good conduct to reinforce it.
- Communities Can:
Provide programs for youth development.
Provide funds and volunteers to support school initiatives.
Establish secure areas for interacting with others.
Measuring the Impact of Social Emotional Learning
How can we determine whether the components of social emotional learning are having an impact? Here are a few signs:
- Enhanced involvement of students
- Reduced disciplinary measures
- Increased emotional intelligence
- Improved interactions between teachers and students
- Good relationships with peers
Assessment instruments such as behavior logs, teacher observations, and self-report questionnaires can offer important information on how effective SEL is.
Challenges in Implementing SEL and How to Overcome Them
Even though SEL is universally acknowledged to be important, several obstacles can prevent it from being implemented successfully:
1. Teachers’ lack of training
The answer is to offer continuing professional development that emphasizes SEL techniques and resources.
2. The Curriculum’s Time Restrictions
Solution: Rather than treating SEL as a stand-alone subject, include it in already-existing courses and practices.
3. Stakeholder Opposition
Solution: Disseminate research with solid data that shows SEL’s long-term emotional and academic advantages.
Conclusion
Social emotional learning encompasses more than simply educational jargon. These are essential life skills that enable people to confidently, empathetically, and resiliently navigate a complicated and changing world.
These five pillars, which range from self-awareness development to responsible decision-making, influence not just academic achievement but also long-term personal and professional fulfillment. A generation of socially conscious and emotionally intelligent people is produced when communities, families, and schools work together to foster these qualities.
Whether you’re a parent helping your child navigate life’s ups and downs or an educator creating a lesson plan, keep in mind that the components of social emotional learning hold the key to a more prosperous, compassionate, and connected future.