Understanding MTSS
The Foundations of MTSS
MTSS encompasses a range of instructional strategies and interventions aimed at meeting the diverse needs of all students. It is built upon several key components:
- Universal Screening: Regular assessments to identify students who may need additional support.
- Data-Based Decision Making: Using data to guide instruction and intervention decisions.
- Progress Monitoring: Continuous assessment of student progress to inform instruction.
- Multi-Tiered Intervention: Providing different levels of support based on the intensity of students’ needs.
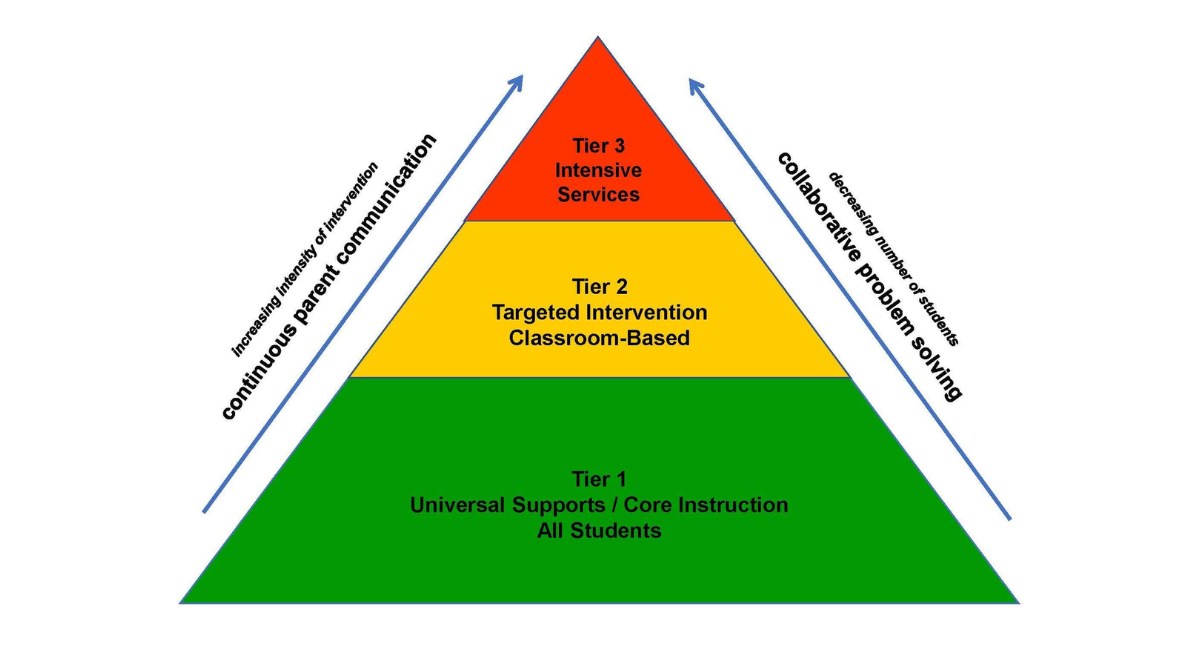
The Three Tiers of MTSS
MTSS is typically divided into three tiers:
- Tier 1: Universal Instruction:
- Description: High-quality, research-based instruction provided to all students in the general education classroom.
- Goal: Ensure that the majority of students achieve academic and behavioral success through effective core instruction.
- Strategies: Differentiated instruction, positive behavior interventions, and supports (PBIS).
- Tier 2: Targeted Group Interventions:
- Description: Additional support for students who are not making adequate progress in Tier 1.
- Goal: Provide targeted interventions to small groups of students who need more support.
- Strategies: Small group instruction, specialized programs, and interventions.
- Tier 3: Intensive Individual Interventions:
- Description: Intensive, individualized interventions for students who continue to struggle despite Tier 2 supports.
- Goal: Address the specific needs of individual students through highly personalized strategies.
- Strategies: One-on-one instruction, intensive skill development programs, and individualized behavior plans.
Also Read: Why Social and Emotional Learning Matters: A Deep Dive
The Importance of MTSS for Teachers
Enhancing Instructional Practices
MTSS encourages teachers to adopt a proactive approach to identifying and addressing student needs. By regularly assessing student performance and utilizing data to guide instruction, teachers can:
- Tailor Instruction: Adjust teaching methods and materials to better suit individual learning styles and needs.
- Improve Student Engagement: Implement engaging and effective teaching strategies that promote active learning and participation.
- Address Learning Gaps: Provide timely interventions that target specific areas where students are struggling, thereby preventing minor issues from becoming major obstacles.
Promoting Equity in Education
One of the core principles of MTSS is its commitment to ensuring that all students have access to high-quality education. By systematically identifying and supporting students who need additional help, MTSS promotes educational equity:
- Reducing Disparities: Address achievement gaps and ensure that all students, regardless of their background or circumstances, have the opportunity to succeed.
- Inclusive Practices: Foster an inclusive classroom environment where diverse learning needs are acknowledged and met.
Supporting Positive Behavior
MTSS also encompasses strategies for promoting positive behavior and social-emotional development. For teachers, this means:
- Creating a Positive Classroom Environment: Implementing positive behavior interventions and supports (PBIS) to encourage appropriate behavior and create a supportive learning environment.
- Addressing Behavioral Issues: Providing targeted interventions for students exhibiting challenging behaviors, thereby reducing disruptions and enhancing the overall classroom climate.
Also Read: What is Strategic Management in Education?
Implementing MTSS in the Classroom
Step-by-Step Guide for Teachers
- Conduct Universal Screening:
- Purpose: Identify students who may need additional support.
- Methods: Use standardized tests, observations, and other assessment tools to gather data on student performance.
- Analyze Data:
- Purpose: Make informed decisions about instruction and intervention.
- Methods: Review assessment data, identify trends, and determine which students need additional support.
- Provide Tiered Instruction:
- Tier 1: Implement high-quality, research-based instruction for all students.
- Tier 2: Provide targeted interventions for small groups of students who need more support.
- Tier 3: Deliver intensive, individualized interventions for students with significant needs.
- Monitor Progress:
- Purpose: Track student progress and adjust interventions as needed.
- Methods: Use formative assessments, progress monitoring tools, and regular check-ins to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions.
- Adjust Interventions:
- Purpose: Ensure that interventions are meeting student needs.
- Methods: Review progress data, modify interventions, and provide additional support as necessary.
Best Practices for Effective MTSS Implementation
- Collaboration:
- Purpose: Foster a collaborative approach among teachers, specialists, and administrators.
- Methods: Regular team meetings, shared planning time, and professional development opportunities.
- Professional Development:
- Purpose: Equip teachers with the knowledge and skills needed to implement MTSS effectively.
- Methods: Ongoing training, workshops, and access to resources on evidence-based practices.
- Family and Community Engagement:
- Purpose: Involve families and the community in supporting student success.
- Methods: Regular communication with parents, community partnerships, and family involvement in intervention planning.
- Sustainability:
- Purpose: Ensure the long-term success of MTSS implementation.
- Methods: Continuous evaluation, data-driven decision-making, and a commitment to ongoing improvement.
Also Read: Empower Your Career with Executive Leadership Training at PMOC
Challenges and Solutions in MTSS Implementation
Common Challenges
- Limited Resources:
- Challenge: Schools may lack the necessary resources, including time, staff, and materials, to implement MTSS effectively.
- Solution: Prioritize resource allocation, seek additional funding, and leverage community partnerships.
- Resistance to Change:
- Challenge: Some educators may be resistant to adopting new practices and approaches.
- Solution: Provide ongoing professional development, highlight the benefits of MTSS, and involve teachers in the planning process.
- Data Management:
- Challenge: Collecting, analyzing, and utilizing data can be time-consuming and complex.
- Solution: Invest in data management systems, provide training on data analysis, and establish clear protocols for data use.
- Consistency and Fidelity:
- Challenge: Ensuring that interventions are implemented consistently and with fidelity can be difficult.
- Solution: Provide clear guidelines, conduct regular fidelity checks, and offer support and feedback to teachers.
Solutions for Effective MTSS Implementation
- Develop a Clear Plan:
- Strategy: Create a detailed implementation plan that outlines goals, strategies, and timelines.
- Benefit: Provides a roadmap for successful implementation and helps ensure that all stakeholders are on the same page.
- Build a Supportive Culture:
- Strategy: Foster a culture of collaboration and support among teachers, administrators, and support staff.
- Benefit: Encourages buy-in and ensures that everyone is working towards common goals.
- Utilize Technology:
- Strategy: Leverage technology to streamline data collection, analysis, and communication.
- Benefit: Saves time, improves accuracy, and enhances the overall efficiency of the MTSS process.
- Engage Stakeholders:
- Strategy: Involve all stakeholders, including teachers, parents, and community members, in the implementation process.
- Benefit: Ensures that everyone is invested in the success of MTSS and provides valuable support and resources.
Also Read: Multi-Tiered Systems of Support (MTSS): Everything You Need to Know
The Impact of MTSS on Student Outcomes
Academic Achievement
MTSS has been shown to significantly improve academic achievement by providing targeted support to students who need it most. By addressing learning gaps early and providing personalized interventions, MTSS helps ensure that all students have the opportunity to succeed.
- Increased Proficiency: Students receive the support they need to reach grade-level proficiency.
- Improved Test Scores: Regular progress monitoring and targeted interventions lead to higher test scores.
- Higher Graduation Rates: By addressing academic challenges early, MTSS helps more students stay on track for graduation.
Behavioral and Social-Emotional Development
In addition to academic support, MTSS also addresses behavioral and social-emotional needs. This comprehensive approach helps create a positive and supportive learning environment, which can lead to:
- Reduced Behavioral Issues: Positive behavior interventions and supports (PBIS) help reduce disruptive behaviors.
- Improved Social Skills: Social-emotional learning (SEL) programs help students develop important social skills.
- Enhanced Emotional Well-Being: Targeted support for social-emotional needs leads to improved emotional well-being and mental health.
Teacher Satisfaction and Professional Growth
For teachers, implementing MTSS can lead to increased job satisfaction and professional growth. By providing the tools and support needed to effectively address student needs, MTSS helps teachers feel more confident and capable in their roles.
- Increased Confidence: Teachers feel more confident in their ability to meet the diverse needs of their students.
- Professional Development: Ongoing training and support provide opportunities for professional growth and development.
- Job Satisfaction: A positive and supportive classroom environment leads to higher job satisfaction and reduced burnout.
Conclusion
MTSS is a powerful framework that provides teachers with the tools and strategies needed to support all students. By adopting a proactive and data-driven approach, MTSS helps ensure that every student has the opportunity to succeed academically and socially. For teachers, understanding and effectively implementing MTSS can transform classroom dynamics and significantly improve student outcomes.
With the right resources, training, and collaboration, teachers can create an inclusive and equitable learning environment where all students thrive. The ongoing commitment to evaluating and refining MTSS practices further solidifies its impact, making it an essential component of modern education systems. By embracing MTSS, educators not only enhance their instructional practices but also contribute to the overall well-being and future success of their students.
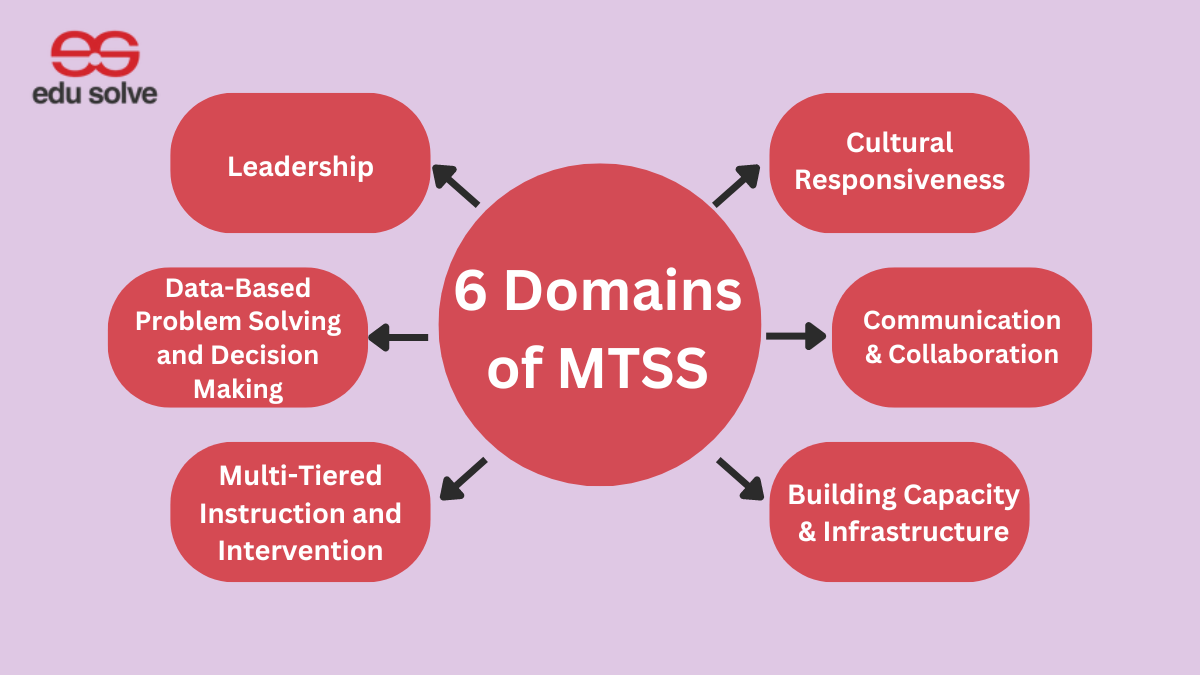
Also Read: What are the 6 Domains of MTSS?